Private Cellular LTE / 5G vs Wi-Fi
In short, Wi-Fi and private cellular have varying applicability and use cases for enterprise connectivity applications. As private cellular is gaining traction with becoming more affordable for enterprises to have their own private cellular network, this whitepaper will help guide decisions with comparing both. In terms of performance, private cellular is better than Wi-Fi for its quality of service, security with SIM authentication and encryption, mobility with handover, better throughput, lower latency and free of Wi-Fi like interference.Private Cellular Overview
Private cellular networks are similar to public cellular networks where you can access the network using a SIM enabled device with a cellular modem like smartphones, dongles, gateways, routers etc. Unlike public networks, a private cellular network is operated by an enterprise and it becomes part of their existing wired and wireless IT infrastructure. Private cellular is gaining more traction recently with the advancement in the technology and virtualization of the cellular stack like radio access network (RAN) a.k.a access points (APs) and network stack (a.k.a Core). This was also accompanied particularly in the USA with FCC’s initiative to make spectrum available specifically for private networks. With this, a warehouse can build and operate its own private cellular network tailored to its own applications and use cases. It is designed to work indoors and outdoors, as well as support backhaul to other network protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRAWAN, Zigbee etc.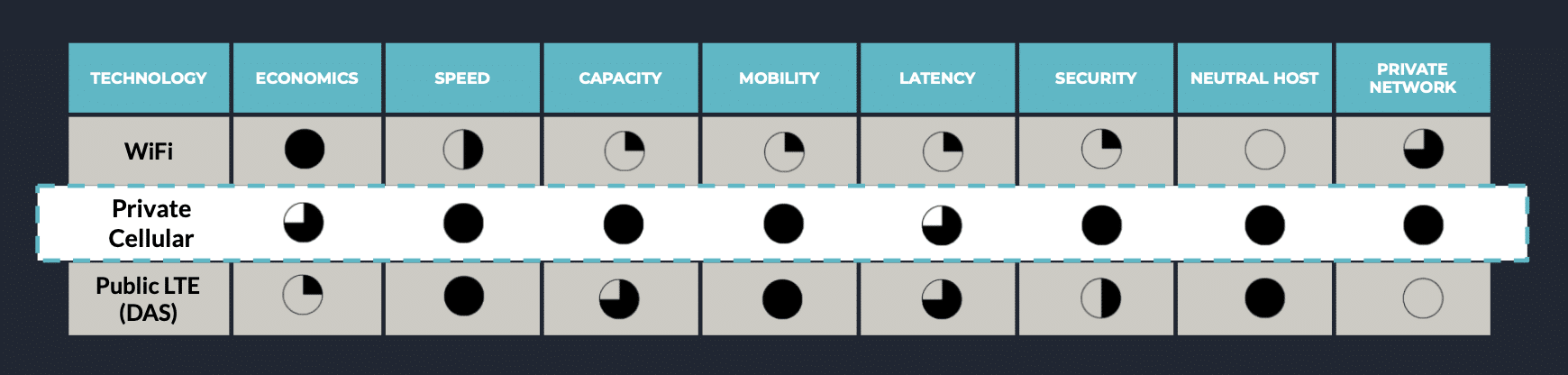
Comparing private cellular with Wi-Fi
Let’s compare private cellular with Wi-Fi across a variety of different metrics.Congestion & Interference
Wi-Fi uses an open, shared, unlicensed spectrum (2.4GHz or 5GHz) that generally suffers from congestion and signal interference. Private cellular uses a centralized service (Spectrum Access Service (SAS)) to facilitate efficient channel management between networks & reduce interference. For example, two buildings/campuses nearby can request different channels so that they don’t interfere with each other. Wi-Fi can be operated by anyone, as simple as you can start a new hotspot on your smartphone and that could cause interference with the existing deployed network. On a Private cellular network, Wi-Fi hotspots can be easily used as clients without any interference between cellular & Wi-Fi RF. Additionally, a private network using CBRS PAL (Priority Access License) spectrum also has protection against any other operator using that spectrum in the area, ensuring interference-free operations. Wi-Fi’s protocol is not designed to proactively identify and reroute signals in the presence of interference. Whereas private cellular networks are an evolution of decades of advancements in cellular networks. Features like self organizing network (SON) and Transmit Power Management (TPM) provide the intelligence to continuously monitor spectrum and adjust the channel & power based on interference to maximize performance.Speed / Bandwidth
Speed is a function of bandwidth, which in the case of Private 5G (100MHz) is by far the fastest, with private LTE (at 40MHz) being a bit slower but still competitive with Wi-Fi (80/160MHz).Latency
Private cellular offers the lowest latency at less than 10 milliseconds for 5G and 30 milliseconds round-trip latency for LTE, and finally followed by Wi-Fi with the highest latency of the three, up to 500 milliseconds.Density / Capacity
Wi-Fi is generally designed to handle just enough concurrent connections for homes or small offices. Private cellular (this benefit also comes from decades of development in public cellular networks) is designed to handle high-capacity commercial and industrial use. While this won’t impact smaller businesses as much, it’s a game changer for larger enterprises who’s operations span vast distances.Coverage
Wi-Fi equipment is generally short-range and covers up to 5K square feet per radio. Cellular equipment takes advantage of greater power levels outdoors and supports lower data rates at the cell edge to easily cover large areas and outdoor environments – up to 16K square feet. indoors and up to 500,000 square feet outdoors, with a private cellular access point. Wi-Fi was never designed to cover large distances, thence a dense Wi-Fi network design with too many access points, repeaters, and bridges are required to make up for the lack of range. In comparison, LTE/5G can be easily scaled through a series of cellular base stations that have much larger coverage area per Access Point. Moreover, GXC’s cellular mesh nodes take it one step further and provide additional coverage and capacity and can be placed throughout a campus or a building where wired infrastructure is not available. (See below section on GXC’s Mesh node: GM01)Mobility
Wi-Fi relies on each device to make the handover / roaming decision across access points as users move around. In contrast to that, Cellular enables centralized coordination of device handover events between access points enabling seamless handoffs by design – facilitating swift connection changes for highly mobile devices.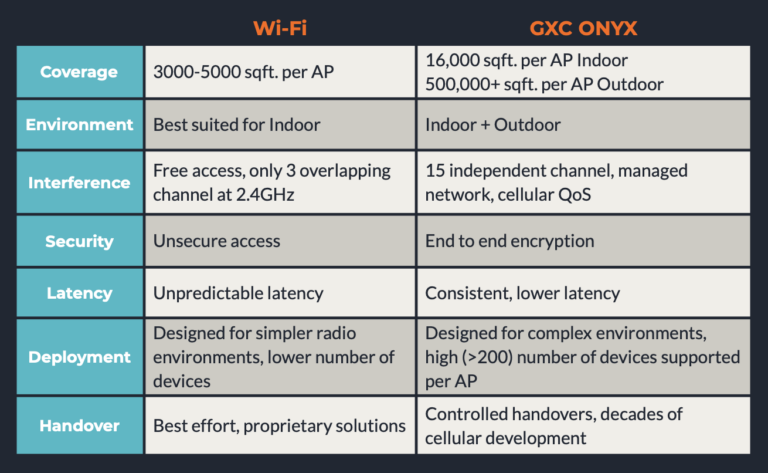
Chances are if you own a cellphone you’ve never noticed when your phone switches its signal from one tower to another. This same seamless transition is possible with private LTE, making it an ideal choice for devices that are on the move or large distances.
Scalability
Solutions based on LTE and 5G technology are designed for better performance when covering large areas, and are more economical for enabling wireless coverage across large facilities, especially outdoors. Also, as the number of access points required are less, the time to get multiple sites installed and operational also goes down.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Private LTE / 5G have built-in quality of service (QoS) mechanisms going from the end user devices all throughout the network to prioritize high-value data for certain applications over all other data. unlike Wi-Fi where this feature is still very basic.
Security
Wi-Fi uses an open spectrum that is frequently targeted by hackers. The option to enable network access without requiring authentication or encryption has always made enterprise IT professionals take extra action in securing the Wi-Fi airwaves and infrastructure that it is part of. Private cellular networks are just that: private. They require an authorized SIM card to enable network access for a specific device – for which centralized encryption of traffic is always enabled.
Unlike Wi-Fi, this creates a secure-by-default environment where only whitelisted devices are allowed to access the network based on the programming of their SIM card. This eliminates the possibility of a wireless password being stolen, leaked, or shared with individuals who are not authorized for access.
Choosing between private cellular and Wi-Fi
Private cellular networks are being adopted everyday and are enabling & improving new use cases for enterprises. They are becoming the go to option for covering large areas and supporting business critical applications.
If the use case requires connecting “carpeted” environments with no strict performance or security requirements, existing Wi-Fi networks will continue to work fine.
For applications with indoor & outdoor use cases, security, mobility, business critical applications, private cellular should be the go to choice for you.
GXC Onyx Mesh
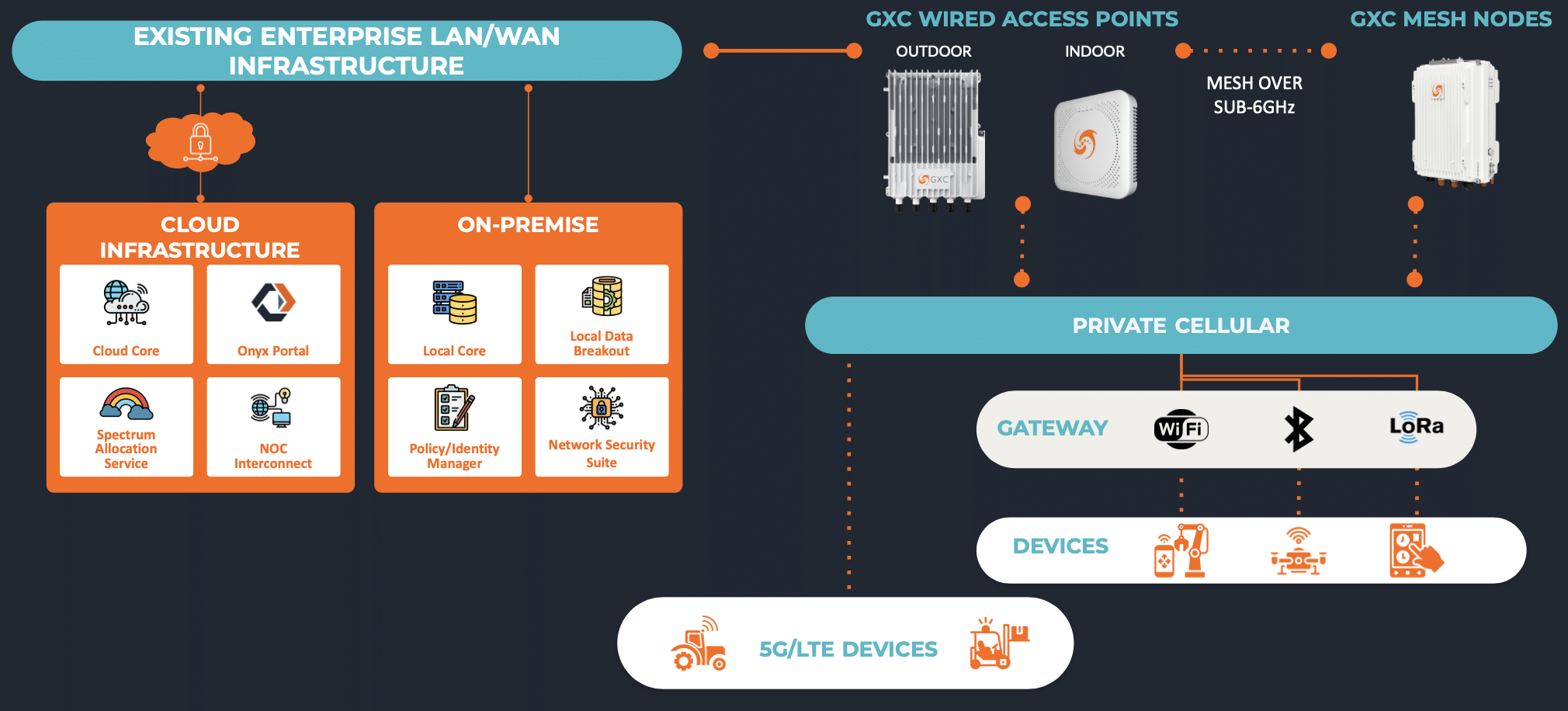
GXC provides a turnkey private network solution for enterprise – GXC ONYX. With Onyx, you get access points (APs), network stack, and a comprehensive network management system (Onyx Cloud), Onyx Edge appliance for a local data breakout and Onyx Mesh.
GXC’s mesh is a LTE/5G RAN mesh where the APs mesh with each other. The key objective of the mesh is to rapidly deploy and extend the coverage of the cellular network. GXC mesh works very similar to the Wi-Fi mesh provided by Nest Wi-Fi, Eero, Plume, but for private cellular.
GXC provides two types of RAN nodes: wired APs and Mesh nodes. Wired APs integrated into the existing infrastructure using fiber/CAT6, while the mesh nodes connect to wired APs over cellular connections forming a mesh.
GXC is the only company in the world that provides a cellular mesh solution allowing you to deploy a high performance & versatile private cellular network that is faster, cheaper and better.
Faster
With GXC’s mesh solution, you can build a private network in the shortest possible time. Use the Onyx wired APs to connect to your existing IT infrastructure wherever you have wired points like fiber, CAT6 available. And then install GXC’s mesh nodes to fill any coverage holes. It eliminates the need to run new fiber/CAT6 infrastructure, especially outdoors which can be time consuming & costly.
Cheaper
Eliminating the need for deploying a wired infrastructure to build a private network eliminates a massive chunk of setup capital infrastructure cost (CapEx). It also makes extending the network cheaper in the future.
Better
A mesh based solution provides for a better connectivity performance vs other alternatives like RF repeaters, or distributed antenna systems. The mesh nodes are able to configure and reconfigure themselves allowing for flexibility of data flow in case of higher traffic and provide reliability in case of node/power failure.
Onyx Mesh Example
Consider a use case of an oil refinery using GXC Onyx solution. Connectivity in a refinery is very complex, with coverage required indoors and outdoors, heavy metal and concrete buildings posing RF propagation challenges. Some of the “refinery cracker” plants (distillation columns) can be over 100 meters high. A Wi-Fi only network could never provide enough signal coverage to connect sensors and devices inside the cracker complex. If one were to estimate the number of Wi-Fi access points required to cover the plant shown in the picture here, it would be over 200 Wi-Fi APs. Moreover, these APs will need to be mounted inside the plant, requiring them each to be C1D2/ATEX compliant, and more importantly requiring CAT6 cable connectivity to backhaul these access points.
Private cellular provides a game changing advantage in this situation. By using GXC’s high power outdoor APs to cover this large complex. GXC’s mesh nodes provide complete coverage to the whole campus with just 3 nodes where only one of them is connected to a wired backhaul, the other nodes are mesh nodes. Best of all, these high power nodes are deployed outside the complex beaming the signal inside the refinery thus staying away from any compliance and backhaul challenges within the facility, yet providing robust and ubiquitous coverage.
GXC’s Onyx solution is generally available and is used by many of its customers in enabling a myriad of applications. The solution is built with the focus of enabling enterprise application and integration of the private cellular network into the existing IT infrastructure.
Please contact us to trial or purchase our solution for your enterprise at sales@gxc.io.



